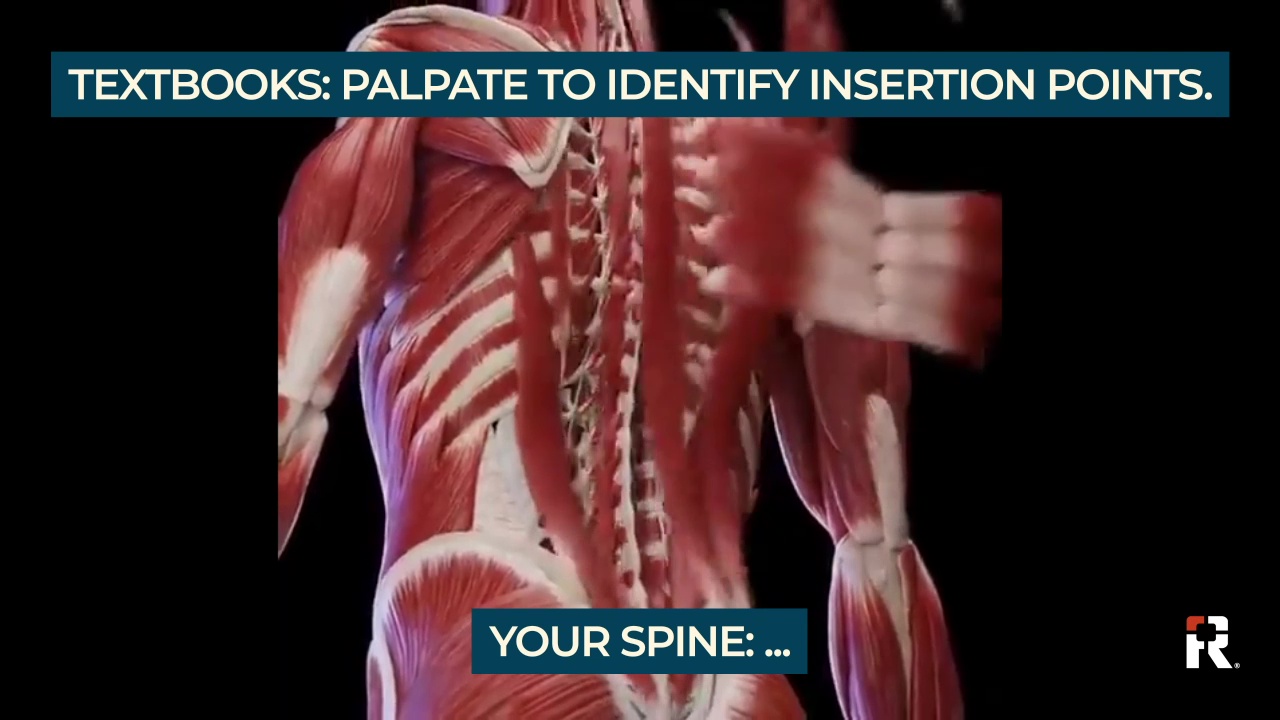
The complexity of spinal muscle systems — comprising multiple overlapping layers while varying widely in tone and bulk — significantly complicates palpation to identify insertion points for neuraxial anesthesia. Muscle dynamics and the presence of adipose and connective tissues obscure spinal landmarks and conceal anatomical abnormalities. These factors, combined with involuntary muscle responses to touch, make it challenging to accurately identify insertion points, emphasizing the need for adjunctive techniques like ultrasound for precise landmark identification.