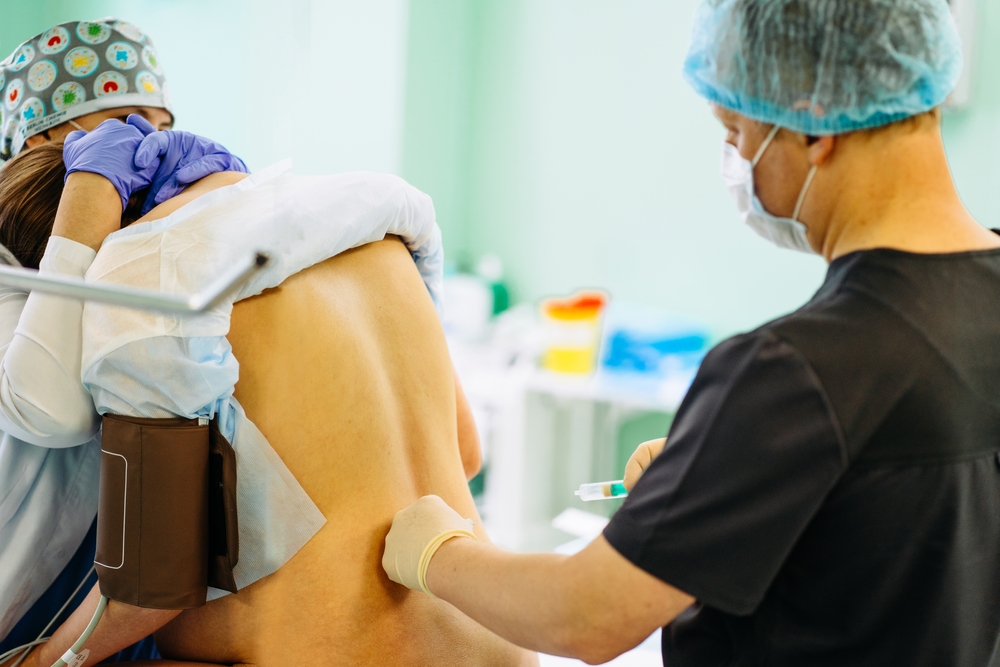
Ultrasound guidance is gaining traction for neuraxial procedures, providing anesthesiologists with enhanced accuracy, precision, and safety. Accuro — a handheld ultrasound guidance device for neuraxial procedures — was designed to integrate seamlessly into clinical practice, making it both convenient and flexible in challenging situations. And this innovative device has lent to new methods for identifying landmarks for needle placement, proving especially useful in cases where patients present with scoliosis and high BMI. But what have these methods taught us? And where do we go next? Today, we have some answers.
Neuraxial anesthesia: Techniques and approaches
Spinal, epidural, and combined spinal-epidural (CSE) anesthesia are key neuraxial techniques used to manage pain and provide muscle relaxation during surgeries and childbirth.
- Spinal anesthesia involves a one-time injection into the subarachnoid space for rapid and profound anesthesia.
- Epidural anesthesia allows for more control, using a catheter to adjust dosing as needed.
- Combined spinal-epidural anesthesia merges both approaches, offering pain relief from spinal anesthesia alongside the flexibility of continuous epidural dosing, making it ideal for scenarios requiring prolonged or adaptable anesthesia management.
Ultrasound guidance enables anesthesiologists and CRNAs to visualize spinal anatomy, improving the precision of needle placement and reducing the risk of complications such as post-dural puncture headaches and spinal hematomas. Assumptions can be based on the observed reduction in the number of needle redirections and increased first-attempt success rate. Ultrasound guidance can enhance both the inline and paramedian approaches to spinal needle placement through a pre-procedural (scouting) approach or real-time needle visualization.
Neuraxial anesthesia: Current methods
Neuraxial anesthesia has evolved from traditional manual methods to advanced, image-guided methods that enhance precision and safety.
- The landmark or palpation method has been the go-to method for decades. With this method, clinicians rely on anatomical landmarks, like the iliac crests and spinous processes, to guide needle placement. Though effective, this approach can be difficult in patients with challenging anatomy — such as occurs with scoliosis or high BMI.
- Pre-procedural ultrasound guidance introduces a new level of accuracy. By using ultrasound to scan the lumbar region and mark the ideal insertion point, clinicians can visualize the underlying anatomy before inserting the needle.
- Automated ultrasound image guidance — with devices like Accuro Neuraxial Guidance — uses image-recognition software to highlight the ideal insertion site. This lessens the need for manual image interpretation, offering real-time feedback and improving precision.
- Real-time needle visualization takes precision a step further by allowing continuous visualization of the needle’s trajectory during insertion. Clinicians can make real-time adjustments, improving both accuracy and safety.
Real-time needle visualization with traditional ultrasound guidance introduces the “Three-Hand Problem,” as it requires the clinician to manage the ultrasound probe, needle, and syringe simultaneously. This workflow complexity — together with the need for improved needle visibility and specialized training in ultrasound image interpretation — has presented barriers to the widespread adoption of this method.
Looking ahead, the next major advancement in neuraxial anesthesia lies in enhancing workflow and real-time needle visualization technology, specifically designed for the unique challenges of neuraxial procedures.
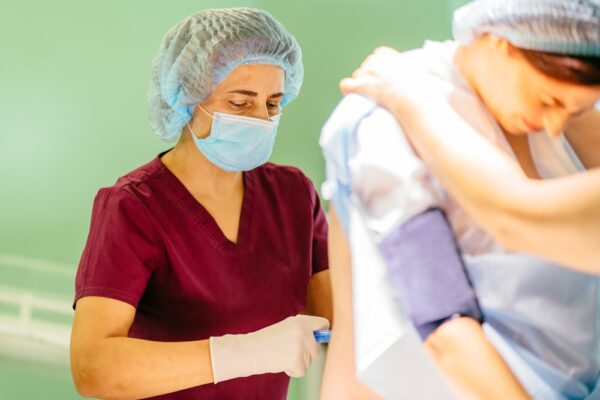
RIVANNA’s solution
With our relentless focus on imaging solutions for spinal needle interventions, RIVANNA — in collaboration with the foundational research of Duke University’s Dr. Charles Y. Kim — has acquired a new patent for an advanced ultrasound-guided needle insertion system designed to improve accuracy and safety in needle-based medical procedures. The system features a dual-array multi-angle probe with uniquely angled ultrasound arrays that enhance needle visibility, along with a detachable needle guide for real-time precision.
- Improved visualization: The dual-array probe integrates data from two transducer arrays for a detailed, wide-field view of the target area.
- Enhanced precision: The detachable needle guide ensures the needle remains within the ultrasound viewing planes throughout insertion, improving accuracy and reducing complications.
- Novel accessibility: The split array facilitates a real-time in-plane needle approach through the center of the probe.
By providing a detachable needle guide that aligns the needle within the optimal ultrasound viewing planes, this new system may allow clinicians a more adaptive and reliable way to guide the insertion of a needle via more sophisticated and fool-proof viewing planes, improved versatility, and more ergonomic needle control. In addition, a hands-free patient drape with bands to support the probe may further simplify workflow, eliminating the need for three hands and reducing complexity.
Follow RIVANNA for more updates!
Ultrasound guidance devices like Accuro have paved the way for the future of neuraxial anesthesia. The road goes ever on, and a new milestone is on the near horizon. As these technologies evolve, staying informed will enable anesthesiologists to become first adopters and advocates for elevated patient care.